
Two notes form an interval. Three or more notes form a chord.
 |
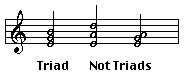
A triad is a three note chord with two thirds stacked on top of one another. The two thirds can be either major or minor, leading to four types of triads. Three notes appearing on three consecutive lines or three consecutive spaces always form a triad.
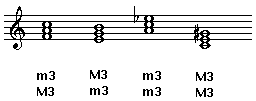 |
 |
|
|
|
Triads do not always appear on three consecutive lines or spaces. The individual notes of the triad can appear in any octave and in any order. As long as the three notes of the chord can be rearranged onto three consecutive lines or spaces, the chord is still called a triad. For example, the three note chord E-C-G shown below is a triad.
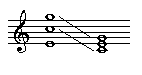 |
When the notes of a chord are played simultaneously it's called block style or chord style.
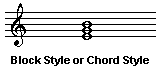 |
When the notes of a chord are played separately it's called broken style or arpeggio style
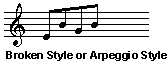 |
A chord written or played in a broken style is called an arpeggio.
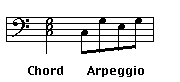 |
When the notes of a triad are written as close together as possible, the triad is said to be in root position, closed spacing.

When the triad is in root position, closed spacing, the individual notes of a triad are given the names: root, third, and fifth. The third and fifth get their names from the interval size formed with the root.
|
|
The root, third, and fifth retain their names even when the notes of the triad are rearranged.
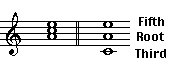
To fully identify a triad you need to determine three things:
The root of a triad is the name of the bottom note when the triad is in root position.
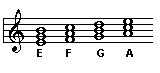 |
There are four triad qualities:
The qualities are determined by type and position of the major and minor thirds of the triad when in root position, closed spacing.

Major Triad
The major triad has a major third on the bottom and a minor third on top.
Minor Triad
The minor triad has a minor third on the bottom and a major third on top.
Diminished Triad
The diminished triad has a minor third on both the bottom and top.
![]()
Augmented Triad
The augmented triad has a major third on both the bottom and top.
![]()
|
Major
|
Minor
|
Diminished
|
Augmented
|
|
|
|
|
|
Triads can appear in three inversions. The inversion is determined by the lowest note of the chord.
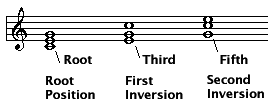
When the notes of a chord appear as close together as possible, the chord is in closed spacing. Closed spacing is also called closed voicing or closed position. Here's a C major chord in root position, first inversion, and second inversion all in closed spacing. The largest interval that appears in closed spacing is the M6 found between the bottom and top notes of second inversion.
 |
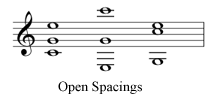
When the notes of a chord are more spread out than in closed spacing, the chord is in open spacing. Open spacing is sometimes called open voicing or open position. Here's a C major chord in root position, first inversion, and second inversion all in open spacing.
 |
Common conventions for labeling chord qualities are:

Other symbols you may see are:

The symbols used to identify inversions are based on the unique interval structures between the chord notes of that inversion.
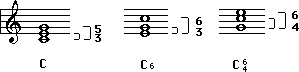
The following chords are all C Major triads. Measure one shows root position, first inversion, and second inversion in closed spacing. Measure two shows root position, first inversion, and second inversion in open spacing.

Question: Name this triad.
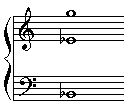
To fully identify a triad you need to determine three things:
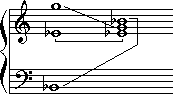
It's Eb, because that's the bottom note when the the triad is in root position )
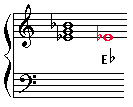
It's Major because the interval structure is Major third on the bottom and minor third on the top.
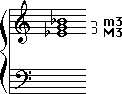
It's second inversion because the fifth is the lowest note.
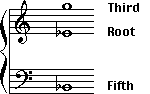
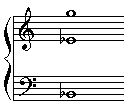
It's F - the directions said so.
2. Quality
An a minor triad has a minor third on the bottom and a major third on the top.
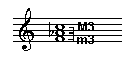
A first inversion triad has the third in the bass.
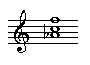
There are multiple answers are all correct. You need the third in the bass. The other two notes can be anywhere.
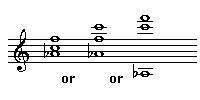
|
Name
|
Notation
|
Lower Third
|
Upper Third
|
Triad
|
|
Major Triad |
|
|||
|
Minor Triad |
|
|||
|
Diminished Triad |
|
|||
|
Augmented Triad |
|
Revised by John Ellinger, Spring 2012.