4.2 Class
CS 312 Audio Programming Winter 2020
Table of Contents
Class 4.2
Lab 4.2 will look at how you can create MIDI sound output directly from your code without using MIDIDisplay_DLS. MIDIDisplay_DLS uses Apple's built in General MIDI synthesizer known as DLS_Synth. DLS stands for DownLoadableSounds and refers to the fact the it is possible to replace Apple's choice of sounds with other 3rd party sound libraries in the Sound Font format. Apple's sounds are licensed from Roland Corporation and are very good.
There is not a lot of documentation about using the DLS_Synth and most of it is based on a ten year old Apple Developer code example called playSoftMidi.cpp. The following steps describe the procedure I followed to compile playSoftMidi.cpp. Once that's been accomplished you'll refactor the code into a CAppleMidiSynth and use it like this.
// stuff packets std::vector<CMidiPacket> vplay; stuffPackets(vplay); ... // play using CAppleMidiSynth CAppleMidiSynth ams; ams.send(vplay);
Mount your course folder using the Go menu in Mac Finder
smb://courses.ads.carleton.edu/COURSES/cs312-00-w20
Execute in Mac Terminal
setup312 <your_carleton_email_name>
Folder structure
After you've mounted your cs312 course folder the mount point is
/Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork/email_name $HOME312 = /Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork/email_name (same as above) Inside $HOME312 are these folders bin common cs312 googletest (the big download from class 3.2) # anything else is ignored in assignment setups
c421_playSoftMIDI
Download playSoftMIDI from Apple
Click the "Download Smaple Code" button.
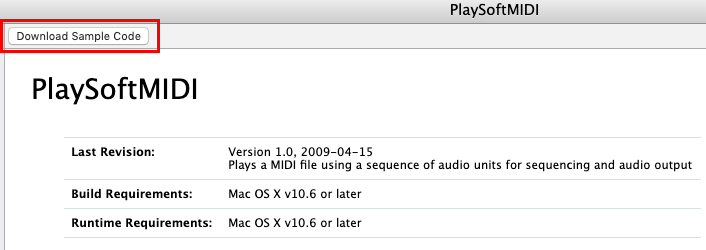
Setup
cd $HOME312 cp ~/Downloads/PlaySoftMIDI.zip . unzip PlaySoftMIDI.zip ls # Make sure the PlaySoftMIDI folder is in $HOME312 cd $HOME312/cs312 mkdir hw42 cd hw42 mkdir c421_playSoftMidi cd c421_playSoftMidi touch CMakeLists.txt mkdir build cp $HOME312/PlaySoftMIDI/main.cpp ./c421_playSoftMidi.cpp
Open c421_playSoftMidi folder as a workspace in vsCode
Open the c421_main.cpp file.
Open vsCode Terminal.
Problems right away
The PROBLEMS tab shows four problems. When trying to compile 10 year old code you can reasonably expect problems.
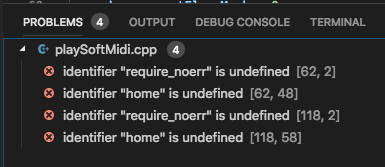
The problems are the result of using an obsolete macro require_noerr that was removed in Xcode 9 (lab uses Xcode 10.x). The require_noerr macro was replaced with __Require_noErr which I found out by googling "Mac OS X require_noerr".
stackoverflow.com
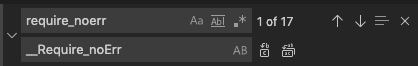
Fix 1.
FIND: require_noerr
REPLACE: __Require_noErr (two underscore prefix)
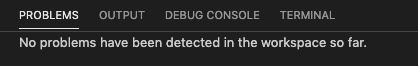
Problems gone. Don't believe it.
Compile 1
#cd $HOME312/cs312/hw42/c421_playSoftMidi cl c421_playSoftMidi.cpp
Problems
Four warnings, many undefined symbols, ending with a link error.
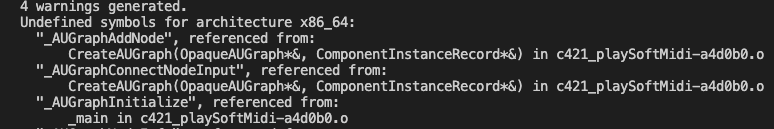
Fix 2.
The link errors occur because the linker cannot find the framework libraries for that match the Audio includes.
These Apple #include files are used but the libraries that implement these files cannot be found by during the link phase.
#include <CoreServices/CoreServices.h> //for file stuff #include <AudioUnit/AudioUnit.h> #include <AudioToolbox/AudioToolbox.h> //for AUGraph
Compile 2
You can use the -frameworks compile flag to include framework libraries on the command line.
cl -framework CoreServices -framework AudioUnit -framework AudioToolbox c421_playSoftMidi.cpp
Progress but still problems
Four warnings left. We'll deal with the warnings one at a time.
Fix 3. 'FSPathMakeRef' warning
Comment out this section (lines 121-134)
Shortcut: Select region then type Command-/.
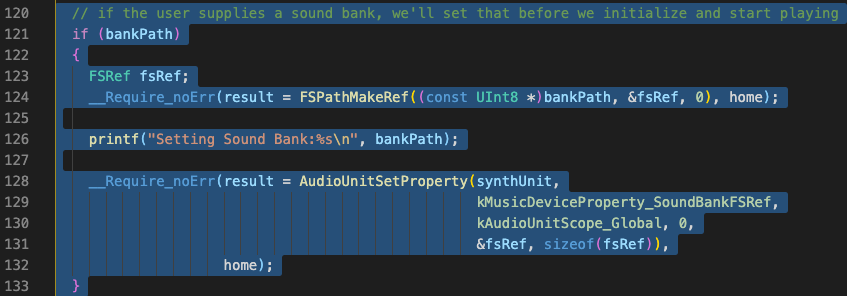
Compile 3
cl -framework CoreServices -framework AudioUnit -framework AudioToolbox c421_playSoftMidi.cpp
Progress, no errors but three warnings
The warnings are all related to the printf(…) statement on line 162.
c421_playSoftMidi.cpp:162:64: warning: values of type 'UInt32' should not be used as format arguments; add an explicit cast to 'unsigned int' instead [-Wformat] printf("Playing Note: Status: 0x%lX, Note: %ld, Vel: %ld\n", noteOnCommand, noteNum, onVelocity); ~~~ ^~~~~~~~~~~~~ %X (unsigned int)
Before we fix the errors execute ./a.out.
You should see this output and hear the C major scale being played.
je$ ./a.out
AudioUnitGraph 0xBC8000:
Member Nodes:
node 1: 'aumu' 'dls ' 'appl', instance 0x80bc8112 O I
node 2: 'aufx' 'lmtr' 'appl', instance 0x80bc8113 O I
node 3: 'auou' 'def ' 'appl', instance 0x80bc8114 O I
Connections:
node 1 bus 0 => node 2 bus 0 [ 2 ch, 44100 Hz, 'lpcm' (0x00000029) 32-bit little-endian float, deinterleaved]
node 2 bus 0 => node 3 bus 0 [ 2 ch, 44100 Hz, 'lpcm' (0x00000029) 32-bit little-endian float, deinterleaved]
CurrentState:
mLastUpdateError=0, eventsToProcess=F, isInitialized=T, isRunning=F
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 60, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 61, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 62, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 63, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 64, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 65, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 66, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 67, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 68, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 69, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 70, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 71, Vel: 127
Playing Note: Status: 0x90, Note: 72, Vel: 127
Fix warnings
The printf(…) command that is part of the C library. We'll replace it using C++ std::cout.
Comment out the printf(…) command (162) and rewrite using std::cout.
// printf("Playing Note: Status: 0x%lX, Note: %ld, Vel: %ld\n", noteOnCommand, noteNum, onVelocity); //clang-format off std::cout << "Playing Note: Status: " << noteOnCommand << " Note: " << noteNum << " Vel: " << onVelocity << std::endl; //clang-format on
Be sure to add #include <iostream> to the include section.
One more fix for consistency with other cs312 homework
FIND: UInt32
REPLACE: uint32_t
Compile 4
cl -framework CoreServices -framework AudioUnit -framework AudioToolbox c421_playSoftMidi.cpp
Run
./a.out
You should hear a scale being played and see the same output as before.
CMakeLists.txt
Here's how you would add Mac framework libraries to a CMakeLists.txt file.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) set(APPNAME "c421_playMIDI") project(${APPNAME}) set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++17 -Wall ") set(SOURCE_FILES c421_playSoftMidi.cpp ) add_executable(${APPNAME} ${SOURCE_FILES}) # add framework libraries to your project. target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework CoreServices") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioUnit") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioToolbox")
Reading
playSoftMIDI code notes
This Overview is from:
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/audiotoolbox/audio_unit_processing_graph_services?language=objc
Overview
Audio Unit Processing Graph Services provide interfaces for representing a set of audio units, connections between their inputs and outputs, and callbacks used to provide inputs. It also enables the embedding of sub (or child) processing graphs within parent graphs to allow for a logical organization of parts of an overall signal chain.
An audio processing graph object (of type AUGraph) is a complete description of an audio signal processing network. Audio Unit Processing Graph Services may manage the instantiated audio units if the AUGraph function is called.
An audio processing graph object may be introspected to get complete information about all of the audio units in the graph. The various node objects (each of type AUNode) in the graph, each representing an audio unit or a sub graph, may be added or removed, and the interactions between them modified.
A graph object’s state can be manipulated in both the rendering thread and in other threads. Consequently, any activities that affect the state of the graph are guarded with locks and a messaging model between any calling thread and the thread upon which the graph object’s output unit is called (the render thread).
A graph object will have a single head node––an output unit. The output unit is used to both start and stop the rendering operations of a graph, and is the dispatch point for the safe manipulation of the state of the graph while it is running.
Here's a version of the playSoftMIDI.cpp code with my comments that will hopefully add a little insight into the code.
OSStatus CreateAUGraph(AUGraph &outGraph, AudioUnit &outSynth) { OSStatus result; /* JE create three nodes for AUGraph Describes signal flow synthNode ==> limiterNode ==> outNode formatted as one line per node variable */ AUNode synthNode; // Apple DLS synth AUNode limiterNode; // avoids clipping AUNode outNode; // speakers AudioComponentDescription cd; cd.componentManufacturer = kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple; cd.componentFlags = 0; cd.componentFlagsMask = 0; /* Create a new audio graph using the reference parameter outGraph the rest of this code fills in details of outGraph because it's a non const reference parameter the newly created outGraph will be available to the code that called CreateAUGraph() */ __Require_noErr(result = NewAUGraph(&outGraph), home); // use the Apple DLSSynth cd.componentType = kAudioUnitType_MusicDevice; cd.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_DLSSynth; // add the DLS synth to the audio graph __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphAddNode(outGraph, &cd, &synthNode), home); /* add a Peak Limiter effect to the graph audio signal data are called samples samples are floating point values from -1.0 to +1.0 if any sample exceeds the range it can cause pops, clicks, and harsh distortion in the output */ cd.componentType = kAudioUnitType_Effect; cd.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_PeakLimiter; // add the Peak Limiter effect to the audio graph __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphAddNode(outGraph, &cd, &limiterNode), home); /* The audio output device Default output is user OS preference setting for sound output */ cd.componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output; cd.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_DefaultOutput; // add the default sound output device audio graph __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphAddNode(outGraph, &cd, &outNode), home); /* Information for later 4.2 homework Notice the statements above are instructions to setup the audio graph They could be used in a class constructor The statements below could be class functions */ // The AUGraphOpen(outGraph) could become a separate class function __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphOpen(outGraph), home); /* Describe signal flow through the audio graph The first line connects synthNode => limiterNode The second line connects limiterNode => outNode */ __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphConnectNodeInput(outGraph, synthNode, 0, limiterNode, 0), home); __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphConnectNodeInput(outGraph, limiterNode, 0, outNode, 0), home); // ok we're good to go - get the Synth Unit... __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphNodeInfo(outGraph, synthNode, 0, &outSynth), home); // If __Require_noErr macro fails we go home. home: return result; }
AUComponent
This output was displayed when you ran ./a.out
Member Nodes: node 1: 'aumu' 'dls ' 'appl', instance 0x842eb112 O I node 2: 'aufx' 'lmtr' 'appl', instance 0x842eb113 O I node 3: 'auou' 'def ' 'appl', instance 0x842eb114 O I Connections: node 1 bus 0 => node 2 bus 0 [ 2 ch, 44100 Hz, 'lpcm' (0x00000029) 32-bit little-endian float, deinterleaved] node 2 bus 0 => node 3 bus 0 [ 2 ch, 44100 Hz, 'lpcm' (0x00000029) 32-bit little-endian float, deinterleaved] CurrentState: mLastUpdateError=0, eventsToProcess=F, isInitialized=T, isRunning=Fh
Member Nodes
Three AudioUnit types were created.
| Node | Bus | Ref | AUComponent.h const |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 'aumu' | kAudioUnitType_MusicDevice |
| 1 | 0 | 'dls ' | kAudioUnitSubType_DLSSynth |
| 1 | 0 | 'appl' | kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple |
| Node | Bus | Ref | AUComponent.h const |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 'aufx' | kAudioUnitType_Effect |
| 2 | 0 | 'lmtr' | kAudioUnitSubType_PeakLimiter |
| 2 | 0 | 'appl' | kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple |
| Node | Bus | Ref | AUComponent.h const |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | 'auou' | kAudioUnitType_Output |
| 3 | 0 | 'def ' | kAudioUnitSubType_DefaultOutput |
| 3 | 0 | 'appl' | kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple |
Connections
The term Bus refers to a feature found on studio mixers where a group of channels can be sent/bussed to one or more submixers.
Say the drums were recorded with five different microphones each going to a separate mixer input. Then those five channel strips could be be balanced independently and sent (bussed) to a drum bus. The drum bus would control the five balanced drum tracks with a single volume knob. In the playSoftMidi output nodes 1-3 are all sent to bus 0.
The output also shows that node1 is sent to node 2 and node 2 is sent to node 3. It's possible to add additional effects into the chain.
SYNTH UNIT ==> PEAK LIMITER EFFECT ==> DEFAULT OUTPUT
The MusicDeviceMIDIEvent(…)
The MusicDeviceMIDIEvent(…) function used in main() sends MIDI messages to the Apple MIDI Synth. You'll notice that it does not support timestamps. In playSoftMIDI code timing is handled using the microsleep system function usleep().
MusicDeviceMIDIEvent(…) is defined in <MusicDevice.h>. The code comments are written in a text markup language using Doxygen format. The Doxygen application produces code documentation for your code. Not covered in this course but Doxygen is used by many open source projects.
/*! @function MusicDeviceMIDIEvent @abstract Used to sent MIDI channel messages to an audio unit @discussion This is the API used to send MIDI channel messages to an audio unit. The status and data parameters are used exactly as described by the MIDI specification, including the combination of channel and command in the status byte. @param inUnit The audio unit @param inStatus The MIDI status byte @param inData1 The first MIDI data byte (value is in the range 0 < 128) @param inData2 The second MIDI data byte (value is in the range 0 < 128). If the MIDI status byte only has one data byte, this should be set to zero. @param inOffsetSampleFrame If you are scheduling the MIDI Event from the audio unit's render thread, then you can supply a sample offset that the audio unit may apply when applying that event in its next audio unit render. This allows you to schedule to the sample, the time when a MIDI command is applied and is particularly important when starting new notes. If you are not scheduling in the audio unit's render thread, then you should set this value to 0 @result noErr, or an audio unit error code */ extern OSStatus MusicDeviceMIDIEvent( MusicDeviceComponent inUnit, UInt32 inStatus, UInt32 inData1, UInt32 inData2, UInt32 inOffsetSampleFrame) API_AVAILABLE(macos(10.0), ios(5.0), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0));
Change the playback insturment
Add this line immediately above the for loop comment in line 156 to change the instrument to Vibraphone.
__Require_noErr(result = MusicDeviceMIDIEvent(synthUnit, 0xC0, 11, 0, 0), home);
Build and run again You should hear the notes played on a Vibraphone.
You may have noticed that the one data byte message 0xC0 was followed by three numbers. Here's what Intellisense Peek Declaration has to say. It seems to be picking up the Doxygen comments in Apple's source code.
@param inData2 The second MIDI data byte (value is in the range 0 < 128). If the MIDI status byte only has one data byte, this should be set to zero. @param inOffsetSampleFrame If you are scheduling the MIDI Event from the audio unit's render thread, then you can supply a sample offset that the audio unit may apply when applying that event in its next audio unit render. This allows you to schedule to the sample, the time when a MIDI command is applied and is particularly important when starting new notes. If you are not scheduling in the audio unit's render thread, then you should set this value to 0
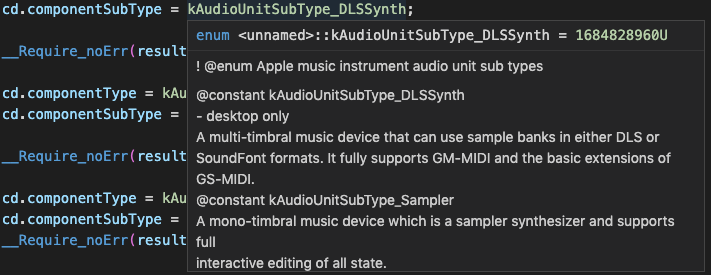
vsCode Intellisense help
Hover the mouse over a term in the vsCode Window and a popup window will appear giving details about the term. In the following picture the term was kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple (line 66).
vsCode Peek Declaration
Right the same term and choose Peek/Peek Declaration and the file where that term is defined will open.
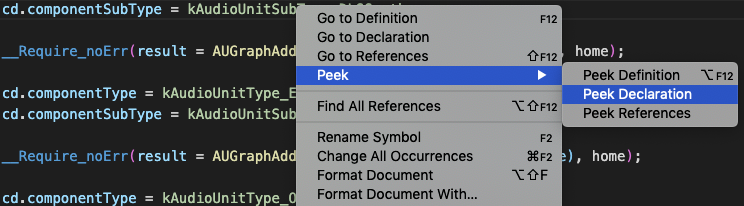
A panel will be superimposed over the code showing where the term was declared.
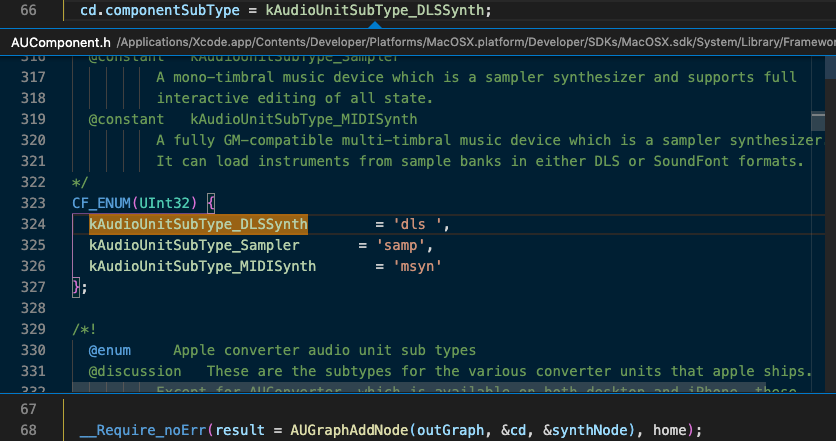
Close the panel with the Escape key.
Apple Audio Documentation
The playSoftMidi code we've been using supports Apple's Audio Unit v2. It may be that this code will not work in the future version of Apple Audio Unit v3 or a future version of Mac OS X. Apple has marked some include files we're using as "deprecated." It is unkwnon when Apple will remove support. The concepts you're learning in this course will be useful for whatever Apple decides to transition to. Apple seems more and more to be moving towards a closed environment merging Mac OS with IOS using their programming language Swift. There are 3rd party cross platform Audio/MIDI libraries available for Mac OS, Windows, and Linux. The two most notable cross platform libraries are PortAudio/PortMidi and RtAudi/RtMidi. We'll be using the cross platform RtMidi and RtAudio libraries in week 7. Here's some reference links.
Audio Unit Programming Guide
Core Audio Overview
Modernizing Your Audio App.pdf
audiounit-v1-v2-support-in-catalina
RtMidi
RtAudio
PortAudio
PortMidi
MIDI and time
When the MIDI specification was created in 1983, the only mention time related to the serial data transmission rate of 31250 bits per second. In 1983 a fast computer ran at 2 MHz. The MIDI transmission rate is 1/64 of 2 MHz. The specification also included a schematic of the electronic circuit necessary to send and receive messages as well as the digital format of those message types. It did not specify when to send the messages. That was left that to the programmer. It wasn't until 1990 when the Standard MIDI File (SMF) specification was published that the concept of musical time appeared. The term delta time was used to refer to the time between MIDI events and was encoded into the SMF as a PPQ (Parts Per Quarter note) value that remained independent of the tempo.
Timestamp types
MIDI timestamps in commercial software are stored as integer milliseconds or microseconds, or floating point seconds. Three timestamp formats are commonly used for MIDI events.
- Chronological
- Delta or difference
- PPQ or Parts Per Quarter note
Here are three examples that would sound the same in each of the three timestamp formats.
Chronological timestamps
This is the MIDIDisplay format we've been using. The first time starts at zero, the millisecond clock is started and each event is scheduled to play when the clock reaches a specified time.
| Time | Message | Process |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | NON | Start the clock, send message, check time |
| 200 | NOF | if ( clock >= 200 ) send message |
| 250 | NON | if ( clock >= 250 ) send message |
| 450 | NOF | if ( clock >= 450 ) send message |
Difference timestamps (delta times)
The time difference between the current timestamp and the previous timestamp.
| Rules |
|---|
| timestamp[0] = vec[0].timestamp |
| timestamp[n] = vec[n].timestamp - vec[n-1].timestamp |
MIDI send procedures are usually implemented using difference timestamps.
Scheduling MIDI messages
Two basic methods for scheduling timestamp messages are Wall Clock Time and Alarm Clock Time.
I just made up those terms.
Wall Clock Time
Here's a recipe for wall clock scheduling.
get the timestamp check the clock while timestamp < clock wait around keep watching the clock when the timestamp > clock send the message immediately. Do not check timestamp == clock because the clock can be off by 1-5 milliseconds.
Alamrm Clock Time
Here's a recipe for alarm clock scheduling.
timestamp[n-1] has just been sent get the timestamp[n] calculate the wait time waitTm = timestamp[n] - timestamp[n-1] milliseconds. delay for waitTm send the message
Changing Tempo
Tempo conversion formula
All CMidiPacket timestamps are stored at a tempo of 60bpm (beats per minute) where one beat = 1000ms = 1second. The formula converting a time based on 60 bpm is given by
\(newTm = tm60bpm * \frac{60}{tempo}\)
Problems with chronological timestamp tempo changes
As long as the tempo never changes you can play a song at any tempo by recalculating the timestamps. The problem happens when you want to change the tempo in the middle of the song. The tempo formula will either cause the timestamps to go backwards in time or jump ahead to the future.
| Tempo | original at 60 bmp | after tempo change | problems |
| 60 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1000 | 1000 | ||
| 2000 | 2000 | ||
| 120 | 3000 | 1500 | backwards |
| 4000 | 2000 | ||
| 5000 | 2500 | ||
| 60 | 6000 | 6000 | jump |
| 7000 | 7000 | ||
| 8000 | 8000 |
Delta times make tempo changes easy
\(newDelta = deltaAt60 * \frac{60}{tempo}\)
Using timestamp differences and the tempo formula lets you to change the tempo at any time during playback. It's only the delta time that changes.
| Tempo | original at 60 bmp | deltaTime | deltaTime after change |
| 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| 2000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| 120 | 3000 | 1000 | 500 |
| 4000 | 1000 | 500 | |
| 5000 | 1000 | 500 | |
| 60 | 6000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 7000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| 8000 | 1000 | 1000 |
You'll use the hw421_CTimerMs delay() function to schedule packets.
4.2 Homework
hw421_CDelayMs
The idea for the CDelayMs class came from code found in TCCP section 15.6, page 200. That code was also used in class 2.3 in the c23_simple_delay.cpp example. In hw421 we'll convert it to a class and copy the files to the common folder. It will replace the usleep() function found in playSoftMIDI.
Setup
cd $HOME312/cs312/hw42 mkdir hw421_CDelayMs cd hw421_CDelayMs mkdir build touch CMakeLists.txt touch CDelayMs.h touch CDelayMs.cpp touch hw421_main.cpp
Open the hw421_CDelayMs folder in vsCode
Copy this code into the appropriate files.
hw421_CDelayMs.h
// hw421_CDelayMs.h #ifndef HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_ #define HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_ #include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <thread> // idea from Stroustroup "A Tour of C++ 2nd Edition" page 200. class CDelayMs { private: uint32_t delay_; bool print_; std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> t0; std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> t1; void milli_time(); void delay(); public: static uint32_t s_tempo; CDelayMs(uint32_t ms, bool print = false); virtual ~CDelayMs(); }; #endif // HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_
hw421_CDelayMs.cpp
// hw421_CDelayMs.cpp #ifndef HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_ #include "hw421_CDelayMs.h" #endif uint32_t CDelayMs::s_tempo = 60; void CDelayMs::milli_time() { t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); std::cout << "# ms:\t\t\t\t"; std::cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(t1 - t0).count() << '\n'; } void CDelayMs::delay() { uint32_t dly = delay_ * 60 / s_tempo; std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(dly)); } CDelayMs::CDelayMs(uint32_t ms, bool print) : delay_{ms}, print_{print} { t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); delay(); } CDelayMs::~CDelayMs() { if (print_) milli_time(); }
hw421_main.cpp
// hw421_main.cpp #ifndef HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_ #include "hw421_CDelayMs.h" #endif #ifndef HW332CMIDIPACKET_H_ #include "hw332_CMidiPacket.h" #endif // DO NOT MODIFY THIS FILE #include <vector> using namespace CMP33; std::vector<CMidiPacket> vplay; void stuffMidiPackets() { // we're going to play an octave of MIDI notes: one a second // every NOF and next NON come at intervals of 1000ms uint32_t tm{0}; uint32_t beat_length{0}; for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) { // Note Ons beat_length = 1000; if (i > 3 && i < 8) beat_length = 500; else if (i > 10) beat_length = 2000; CMidiPacket mp(tm, 0x90, 60 + i, 127); vplay.push_back(mp); // Note Offs tm += beat_length; mp.set_timestamp(tm); // 0 NOF 1000 NOF 2000 NOF etc mp.set_data2(0); vplay.push_back(mp); } } // Instead of playing sound which you'll do later in hw42 // here we're just sending packets to std::cout using timestamp delays void send(const CMidiPacket &mp) { // a static variable maintains its value between function calls // it's needed for calculating the difference between timestamp [n] and [n-1] static uint32_t prevTm{0}; // calculate delay uint32_t ms_delay = mp.get_timestamp() - prevTm; prevTm = mp.get_timestamp(); // reset prevTm for next fn call // create timer delay and send the packet CDelayMs timer(ms_delay, true); // true = print time in ms std::cout << mp; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { stuffMidiPackets(); for (auto itr : vplay) send(itr); }
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) set(APPNAME "c421_playMIDI") project(${APPNAME}) set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++17 -Wall ") set(SOURCE_FILES c421_playSoftMidi.cpp ) add_executable(${APPNAME} ${SOURCE_FILES}) # add framework libraries to your project. target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework CoreServices") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioUnit") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioToolbox")
compile and run
Output
The output shown is in milliseconds and is slightly different on every run but is generally within 0-5 milliseconds.
[100%] Built target hw421_delayTest 0 90 60 127 # ms: 0 1000 90 60 0 # ms: 1000 1000 90 61 127 # ms: 0 2000 90 61 0 # ms: 1003 2000 90 62 127 # ms: 0 3000 90 62 0 # ms: 1005 3000 90 63 127 # ms: 0 4000 90 63 0 # ms: 1004 4000 90 64 127 # ms: 0 4500 90 64 0 # ms: 501 4500 90 65 127 # ms: 0 5000 90 65 0 # ms: 502 5000 90 66 127 # ms: 0 5500 90 66 0 # ms: 501 5500 90 67 127 # ms: 0 6000 90 67 0 # ms: 500 6000 90 68 127 # ms: 0 7000 90 68 0 # ms: 1003 7000 90 69 127 # ms: 0 8000 90 69 0 # ms: 1003 8000 90 70 127 # ms: 0 9000 90 70 0 # ms: 1001 9000 90 71 127 # ms: 0 11000 90 71 0 # ms: 2003 11000 90 72 127 # ms: 0 13000 90 72 0 # ms: 2001
Assignment 421
The solutions to hw421_CDelayMs were accidentally put on the class web page during class. I've updated the code slightly but it should build and run the way it is. Your assignment is to build and run it using cmake. Then copy the hw421_CDelayMs.h and hw421_CDelayMs.cpp files to the common folder so they will be available for future assignments.
Automatic grade of 100 if these files are in your course common folder. A freebee.
- Copy hw421_CDelayMs.h to $HOME/312/common
- Copy hw421_CDelayMs.cpp to $HOME/312/common
hw422_CAppleMidiSynth
Setup Execute these commands.
cd $HOME312/cs312/hw42 mkdir hw422_CAppleMidiSynth cd hw422_CAppleMidiSynth mkdir build touch CMakeLists.txt touch hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h touch hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp touch hw422_main.cpp
You'll also need these these files present in your common folder
- hw332_CMidiPacket
- hw421_CDelayMs
Copy this code into their appropriate files.
hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h
// hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h #ifndef HW422_CAPPLE_MIDISYNTH_H_ #define HW422_CAPPLE_MIDISYNTH_H_ #include <CoreServices/CoreServices.h> //for file stuff #include <AudioUnit/AudioUnit.h> #include <AudioToolbox/AudioToolbox.h> //for AUGraph #ifndef HW332_CMIDIPACKET_H_ #include "hw332_CMidiPacket.h" #endif #include <vector> // DO NOT MODIFY using namespace CMP33; class CAppleMidiSynth { public: CAppleMidiSynth(); virtual ~CAppleMidiSynth(); CAppleMidiSynth(const CAppleMidiSynth &) = default; CAppleMidiSynth(CAppleMidiSynth &&) = default; CAppleMidiSynth &operator=(const CAppleMidiSynth &) = default; CAppleMidiSynth &operator=(CAppleMidiSynth &&) = default; // three overridden send methods void send(uint32_t waitTm, uint8_t st, uint8_t d1, uint8_t d2); void send(const CMidiPacket &mp); void send(const std::vector<CMidiPacket> &vmp); private: AUGraph outGraph; AudioUnit outSynth; }; #endif // HW531_CAPPLEMIDISYNTH_H_
hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp
You need to finish.
// hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp #ifndef HW422_CAPPLE_MIDISYNTH_H_ #include "hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h" #endif #ifndef HW421_CDELAYMS_H_ #include "hw421_CDelayMs.h" #endif // #include <AssertMacros.h> CAppleMidiSynth::CAppleMidiSynth() { // taken from c411_PlaySoftMIDI /*=============== From CreateAUGraph() =============== Copy/paste everything from: OSStatus result; to // ok we're good to go - get the Synth Unit... __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphNodeInfo(outGraph, synthNode, 0, &outSynth), home); ======================================================*/ /*=============== From main() =============== // ok we're set up to go - initialize and start the outGraph __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphInitialize(outGraph), home); CAShow(outGraph); // prints out the outGraph so we can see what it looks like... __Require_noErr(result = AUGraphStart(outGraph), home); ======================================================*/ /*================= JE modification =================== home: if (result == noErr) std::cout << "CAppleMidiSynth() success\n"; else std::cout << "Failed to construct CAppleMidiSynth()\n"; ======================================================*/ } CAppleMidiSynth::~CAppleMidiSynth() { if (outGraph) { // Stop and Dispose AUGraph } } void CAppleMidiSynth::send(uint32_t waitTm, uint8_t st, uint8_t d1, uint8_t d2) { // Called by the next two functions // waitTm is calculated by them CDelayMs d(waitTm, false); MusicDeviceMIDIEvent(outSynth, st, d1, d2, 0); } void CAppleMidiSynth::send(const CMidiPacket &mp) { // You know now_time and previous_time // Difference is wait time // call CAppleMidiSynth::send(uint32_t waitTm, uint8_t st, uint8_t d1, uint8_t d2) // update previous_time } void CAppleMidiSynth::send(const std::vector<CMidiPacket> &vmp) { // figure it out }
hw422_main.cpp
You need to finish.
// hw422_main.cpp #ifndef HW422_CAPPLE_MIDISYNTH_H_ #include "hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h" #endif #ifndef HW332_CMIDIPACKET_H_ #include "hw332_CMidiPacket.h" #endif #ifndef HW421_CDELAY_MS_H_ #include "hw421_CDelayMs.h" #endif #include <vector> // Do not modify stuffPackets void stuffPackets(std::vector<CMidiPacket> &v) { // brute force CMidiPacket mp = {0, 0x90, 60, 100}; //C v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {1000, 0x90, 62, 100}; //D v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {2000, 0x90, 64, 100}; //E v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {3000, 0x90, 65, 100}; //F v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {4000, 0x90, 67, 100}; //G v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {5000, 0x90, 69, 100}; //A v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {6000, 0x90, 71, 100}; //B v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF mp = {7000, 0x90, 72, 100}; //C v.push_back(mp); //NON mp.set_timestamp(mp.get_timestamp() + 1000); mp.set_data2(0); v.push_back(mp); //NOF } // end Do not modify stuffPackets int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { // main expects exactly one parameter for tempo /* display usage message "Usage:\n\thw422_cams <tempo>\n" exit not exactly one parameter set CDelayMs::s_tempo to argv[1] display error message if tempo range is outside 20-300 exit if tempo is too low or too high */ // stuff packets std::vector<CMidiPacket> vplay; stuffPackets(vplay); // play using CAppleMidiSynth CAppleMidiSynth ams; ams.send(vplay); return 0; }
CMakeLists.txt
Copy/paste
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) set(APPNAME "amsTest") project(${APPNAME}) set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++17 -Wall ") # JE sets FOR_CLASS to 0 # YOU set FOR_CLASS to 1 set(FOR_CLASS 0) if(${FOR_CLASS}) set( HOME "/Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork/<your_email_name>" ) elseif(NOT ${FOR_CLASS}) set( HOME "/Users/je/cs312/_cs312") endif(${FOR_CLASS}) set(COMMON "${HOME}/common") set(SOURCE_FILES ${COMMON}/hw332_CMidiPacket.cpp ${COMMON}/hw421_CDelayMs.cpp hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp hw422_main.cpp ) include_directories(${COMMON}) add_executable(${APPNAME} ${SOURCE_FILES}) target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework CoreServices") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioUnit") target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-framework AudioToolbox")
Build and run using cmake
cmake .. && make && ./amsTest #ams AppleMIDISynth
Assignment 422
Implement the missing code. Build and run using cmake. It's working when you hear the C Major scale.
- Copy hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h to $HOME/312/common
- Copy hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp to $HOME/312/common
Hw423 and future assignmentes will use them.
hw423_CScalesTrio
This project uses everything we've covered so far.
Feb 2, 2020 important changes added for using class CMidiTrack
hw423_CScalesTrio was not working with hw413_CMidiTrack
Code 413 wrote to std::cout in order create a CMidiPacket list that could be copied and pasted into MIDIDisplay_DLS.
Code 413 used these functions to write to std::cout
- send_non
- send_nof
- send_patch
- send_volume
- send_pan
- send_expression
Code 423 needs to write to std::vector<CMidiPacket> vtrk defined as a public member variable in CMidiTrack.
Code 423 changed send_name to push_name in order to make it clear that your stuffing the vector vtrk
- push_non
- push_nof
- push_patch
- push_volume
- push_pan
- push_expression
Setup
This is the original setup script. It should still be valid if you've already started work on hw423_CScalesTrio.
cd $HOME312/cs312/hw42 mkdir hw423_CScalesTrio && cd hw423_CScalesTrio # CMake stuff touch CMakeLists.txt mkdir build touch hw423_CAltoTrack.cpp touch hw423_CAltoTrack.h touch hw423_CBassTrack.cpp touch hw423_CBassTrack.h touch hw423_CSopranoTrack.cpp touch hw423_CSopranoTrack.h touch hw423_main.cpp cp $HOME312/cs312/hw41/hw413_CScalesTrack/hw413_CScalesTrack.h ./hw423_CScalesTrack.h cp $HOME312/cs312/hw41/hw413_CScalesTrack/hw413_CScalesTrack.cpp ./hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp sed -i '' s/HW413_CSCALESTRACK_H_/HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_/g ./hw423_CScalesTrack.h sed -i '' 's/hw413_CScalesTrack.h/hw423_CScalesTrack.h/g' ./hw423_CScalesTrack.h sed -i '' s/HW413_CSCALESTRACK_H_/HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_/g ./hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp sed -i '' 's/hw413_CScalesTrack.h/hw423_CScalesTrack.h/g' ./hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp
Execute these commands to create hw423_CMidiTrack
########## NEW 2/2/2020 cd $HOME312/common cp hw413_CMidiTrack.cpp hw423_CMidiTrack.cpp cp hw413_CMidiTrack.h hw423_CMidiTrack.h # change includes and header guards sed -i '' s/HW413_/HW423_/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/hw413_/hw423_/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* # change send_name to push_name sed -i '' s/send_non/push_non/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/send_nof/push_nof/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/send_patch/push_patch/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/send_volume/push_volume/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/send_pan/push_pan/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* sed -i '' s/send_expression/push_expression/g hw423_CMidiTrack.* ############ END NEW
Note:
If you've already started hw423_CScalesTrack you'll need go through the include sections of every file and make these changes.
OLD
#ifndef HW413_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw413_CMidiTrack.h" #endif
NEW
#ifndef HW423_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CMidiTrack.h" #endif
You'll also have to rename the send_non() and other similar functions that begin with send_ to push_.
The compiler will catch these errors once you've made the include changes.
If you haven't started work on hw423_CScalesTrio the changes have already been made in the following files.
CScalesTrack modifications
hw423_CScalesTrack.h
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
Add this code after the end of the SCALE NOTES section and just above the closing #endif statement
// hw423_CScalesTrack.h #ifndef HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_ #define HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_ #ifndef HW423_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CMidiTrack.h" #endif // DO NOT MODIFY THIS CODE class CScalesTrack : public CMidiTrack { public: std::vector<int> vscale; std::vector<int> vrhythm; CScalesTrack(uint32_t beginTime, uint32_t endTime, uint8_t noteoffset, uint8_t channel, uint8_t patch, uint8_t volume, uint8_t pan); int get_note(); // choose a random scale note void write_scales_track(); virtual void write_track(); // must define it was declared pure virtual in CMidiTrack }; // SCALE NOTES // See class web page for more information // You can add your own to the list. // clang-format off const std::vector<int> vmajor_pentatonic{0, 2, 4, 7, 9, 12}; // Major pentatonic const std::vector<int> vminor_pentatonic{0, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12}; // Minor pentatonic const std::vector<int> vragtime{0, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 12}; // Ragtime scale const std::vector<int> vrock_blues{0, 3, 4, 7, 9, 10, 12}; // Rock blues Scales const std::vector<int> vminor_blues{0, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12}; // Minor blues Scales const std::vector<int> v6note_blues{0, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12}; // 6 note blues Scales const std::vector<int> v7note_blues{0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 12}; // 7 note blues Scales const std::vector<int> vmideast{0, 1, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11, 12}; // Middle Eastern scale const std::vector<int> vjapanese{0, 1, 5, 7, 8, 12}; // Japanese scale const std::vector<int> voctotonic{0, 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12}; // Octotonic jazz scale half step, whole step const std::vector<int> vwholetone{0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}; // Whole tone, whole step, whole step const std::vector<int> vflamenco{0, 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, 12}; // Flamenco const std::vector<int> vphrygian_dominant{0, 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12}; // Phrygian dominant // clang-format ON ////// JE ADDED for hw423 /* DURATION VALUES duration values are expressed in milliseconds with a quarter note = 1000 at a tempo of 60 beats per minute. */ const std::vector<int> vrhythm0 = {500, 250, 250, 500}; // the original hw423_CScalesTrack pattern // je additional patterns const std::vector<int> vrhythm1 = {250, 250, 500}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm2 = {500, 500}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm3 = {250, 500, 1000}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm4 = {125, 250, 500, 1000}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm5 = {333, 667, 1000}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm6 = {333, 333, 334, 667}; const std::vector<int> vrhythm7 = {333, 333, 333, 333, 667, 667, 1000}; #endif // HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_
hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp
Setup copied the latest version of hw413_CScalesTrack.cpp in your cs312/hw41 folder. If you've been working outside this folder you'll have to update hw413_CScalesTrack.cpp with your latest changes.
Copy this code to the appropriate files.
hw423_CSopranoTrack.h
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
//hw423_CSopranoTrack.h #ifndef HW423_CSOPRANOTRACK_H #define HW423_CSOPRANOTRACK_H #ifndef HW423_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CMidiTrack.h" #endif #ifndef HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CScalesTrack.h" #endif class CSopranoTrack : public CScalesTrack { public: CSopranoTrack(uint32_t beginTime, uint32_t endTime, uint8_t noteoffset, uint8_t channel, uint8_t patch, uint8_t volume, uint8_t pan); void write_track() override; }; #endif // HW423_CSopranoTrack_H
hw423_CAltoTrack.h
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
// hw423_CAltoTrack.h #ifndef HW423_CALTOTRACK_H_ #define HW423_CALTOTRACK_H_ #ifndef HW423_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CMidiTrack.h" #endif #ifndef HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CScalesTrack.h" #endif class CAltoTrack : public CScalesTrack { public: CAltoTrack(uint32_t begintime, uint32_t endTime, uint8_t noteoffset, uint8_t channel, uint8_t patch, uint8_t volume, uint8_t pan); void write_track() override; }; #endif // HW423_CALTOTRACK_H_
hw423_CBassTrack.h
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
// hw423_CBassTrack.h #ifndef HW423_CBASSTRACK_H #define HW423_CBASSTRACK_H #ifndef HW423_CMIDITRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CMidiTrack.h" #endif #ifndef HW423_CSCALESTRACK_H_ #include "hw423_CScalesTrack.h" #endif class CBassTrack : public CScalesTrack { public: CBassTrack(uint32_t begintime, uint32_t endTime, uint8_t noteoffset, uint8_t channel, uint8_t patch, uint8_t volume, uint8_t pan); void write_track() override; }; #endif // CBASSTRACK_H
hw423_CSopranoTrack.cpp
Your job. Kinda like this.
#ifndef HW423_CSOPRANOTRACK_H #include "hw423_CSopranoTrack.h" #endif // The random functions have been moved to a utility unit. #ifndef HW411_RAND_INT_H_ #include "hw411_rand_int.h" #endif CSopranoTrack::CSopranoTrack(uint32_t beginTime, uint32_t endTime, uint8_t noteoffset, uint8_t channel, uint8_t patch, uint8_t volume, uint8_t pan) : CScalesTrack(beginTime, endTime, noteoffset, channel, patch, volume, pan) { } void CSopranoTrack::write_track() { // set the patch, volume, and pan // Note that it's calling the write_track() function in the parent class CScalesTrack::write_track(); // fill the CMidiPacket vector vtrk that was inherited from CMidiTrack class // should be similare to what you did for hw413_CScalesTrack }
hw423_CAltoTrack.cpp
Your job.
hw423_CBassTrack.cpp
Your job.
hw423_main.cpp
Pseudo code
#ifndef XXX_H_ #include "necessary.h" #endif etc. int main() { // declare soprano track parameters // uint16_t beginTime = ; // uint16_t startNote = ; // uint16_t chan = ; // uint16_t patch = ; // uint16_t vol = ; // uint16_t pan = ; // Create the soprano track CSopranoTrack sop_trk(beginTime, endtime, startNote, chan, patch, vol, pan); // declare alto track parameters that are different from soprano // beginTime = ; // startNote = ; // chan = ; // patch = ; // vol = ; // pan = ; // Create alto track CAltoTrack alto_trk(beginTime, endtime, startNote, chan, patch, vol, pan); // declare bass track parameters that are different from soprano // beginTime = ; // startNote = ; // chan = ; // patch = ; // vol = ; // pan = ; // Create bass track CBassTrack bass_trk(beginTime, endtime, startNote, chan, patch, vol, pan); // set the scale and rhythm duration pattern for each track // you can choose from the patterns in hw423_CScalesTrack or create your own // sop_trk.vscale = ; // sop_trk.vrhythm = ; // alto_trk.vscale = ; // alto_trk.vrhythm = ; // bass_trk.vscale = ; // bass_trk.vrhythm = }; // Write the three tracks // create the playback vector vplay // use std::copy for sop_trk, alto_trk, bass_trk with td::back_inserter(vplay) // vector vplay now holds all elements of sop, alto, bass vectors // sort vplay vector // it will use your operator< (less) routine // Set the playback tempo // This is the variable you use // The number (120) is passed in from the command line CDelayMs::s_tempo = 120; // create the CAppleMidiSynth object CAppleMidiSynth ams; for (auto itr : vplay) { std::cout << itr; // send CMidiPackets to cout while playing ams.send(itr); // play the CMidiPacket } }
CMakeLists.txt
Your job.
Assignment 423
Requirements for hw423
- Must use the new hw423_CMidiTrack.cpp and hw423_CMidiTrack.h files in the common folder.
- Build and compile with cmake.
- All NON's must be matched with a NOF so there are no "stuck" notes.
- Three tracks, soprano, alto, bass
- Each track must be on a different MIDI channel.
- Each track must be assigned a different instrument (patch change).
- One track must be panned left (Control change 0xBn, 10, 0=left).
- One track must be panned center (Control change 0xBn, 10, 64=center).
- One track must be panned right (Control change 0xBn, 10, 127=right).
- You may set the relative volumes of each track at startup (Control change 0xBn, 7, 0-127).
- Each track must use a different pitch range (scale note offset for Soprano, Alto, Bass).
- Each track may use the same or different scale. You can make up your own scales.
- Each track may use different beat patterns. You can make up your own beat patterns.
- Each track should end at roughly the same time around timestamp 64000.
- Each track starts at a different time 0, 8000, and 16000.
- You must have exactly one command line option to set the starting tempo.
- You have the option of changing or not changing the tempo in the software.
- The song must playback using CAppleMidiSynth.
- You must be happy with the results.
- "If it sounds good, it IS good."
Experiment with scales and rhythm patterns. Copy your favorite pattern to a file named "hw423_fave.txt" and include it as part of the handout.
Files needed
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
$HOME312/common ├── hw332_CMidiPacket.cpp ├── hw332_CMidiPacket.h ├── hw411_rand_int.cpp ├── hw411_rand_int.h ├── hw421_CDelayMs.cpp ├── hw421_CDelayMs.h ├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp ├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h ├── hw423_CMidiTrack.cpp └── hw423_CMidiTrack.h hw423_CScalesTrio ├── CMakeLists.txt ├── build ├── hw423_CAltoTrack.cpp ├── hw423_CAltoTrack.h # subclass of CScalesTrack ├── hw423_CBassTrack.cpp ├── hw423_CBassTrack.h # subclass of CScalesTrack ├── hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp # minor modification of hw413 ├── hw423_CScalesTrack.h # minor modification of hw413 ├── hw423_CSopranoTrack.cpp ├── hw423_CSopranoTrack.h # subclass of CScalesTrac └── hw423_main.cpp
Submission Format
Feel free to email /jellinge@carleton.edu/ on any part of the homework that is unclear to you. Chances are if you have questions other students do too. I will answer those questions by email to everyone in the class. The original sender will remain anonymous. I have tried to provide clues to the homework in the web pages, reading assignments, and labs. Sometimes what seems obvious to me is not obvious to students just learning C++. Create a folder named */hwNN_LastnameFirstname1_LastnameFirstname2/*. \\ Substitute your name and your partner's name for LastnameFirstname1_LastnameFirstname2. *Remember* - Boilerplate header at top of every file. - Make sure your program compiles before submitting. \\ - Programs that compile and produce partially correct output will be graded. \\ - You can send notes to me in your homework files by enclosing them in block comments.\\ - Programs that do not compile get an automatic F (59%). - Each partner must submit identical homework folders to the course Hand-in folder. \\ - If only one partner submits the homework send me an email explaining why. - Empty your /build/ or /build-debug/ folders using the command /emptyBuildFolder.sh/ - Only include .h, .cpp, Makefiles, CMakeLists.txt - Do not include these folders/files \\ .git \\ .vscode \\ - Double check for the above two folders using this command \\ #+begin_src sh ls -a hwNN_LastnameFirstname1_LastnameFirstname2 # if either .git or .vscode exist in the folder you're submitting remove them with # rm -fR .git # rm -fR .vscode #+end_src
Hand-in
Feb 2, 2020 changes added. Now uses hw423_CMidiTrack.h
$HOME312/common
├── hw332_CMidiPacket.cpp
├── hw332_CMidiPacket.h
├── hw411_rand_int.cpp
├── hw411_rand_int.h
├── hw421_CDelayMs.cpp
├── hw421_CDelayMs.h
├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp
├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h
├── hw423_CMidiTrack.cpp
└── hw423_CMidiTrack.h
$HOME312/cs312/hw42
├── hw421_CDelayMs
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── build
│ ├── hw421_CDelayMs.cpp
│ ├── hw421_CDelayMs.h
│ └── hw421_main.cpp
├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── build
│ ├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.cpp
│ ├── hw422_CAppleMidiSynth.h
│ └── hw422_main.cpp
└── hw423_CScalesTrio
├── hw423_fave.txt
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── build
├── hw423_CAltoTrack.cpp
├── hw423_CAltoTrack.h
├── hw423_CBassTrack.cpp
├── hw423_CBassTrack.h
├── hw423_CScalesTrack.cpp
├── hw423_CScalesTrack.h
├── hw423_CSopranoTrack.cpp
├── hw423_CSopranoTrack.h
└── hw423_main.cpp
Created: 2020-02-01 Sat 10:08