CS 312 - Week 1.2
CS 312 Audio Programming Winter 2020
Table of Contents
Step by step start up in WCC
Do not open Terminal yet.
Mount your courses folder for CS312
In Mac Finder choose Go menu/Connect to Server
Enter
smb://courses.ads.carleton.edu/COURSES/cs312-00-w20
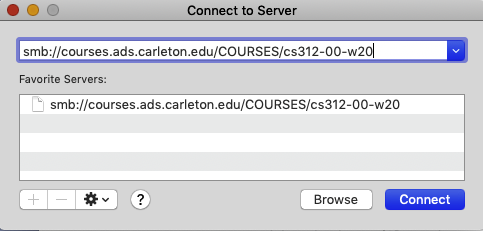
The term COURSES should only appear when you mount cs312-00-w20.
The Mac mount location is /Volumes/cs312-00-w20
Check in Mac Finder
Type Command-Shift-G
You can use this to see normally hidden files like usr/local
Enter /Volumes
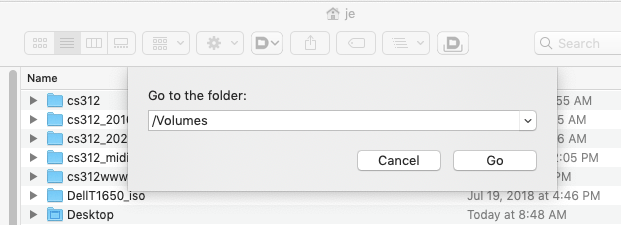
Is cs312-00-w20 listed? It should be.
Is COURSES listed? It should not be.
Display hidden dot files
Open your home folder in Mac Finder and type
Command-Shift-. (period) to toggle the display of the hidden "dot files"
Filenames that begin with a period.
You should see these three files:
- .bash_profile
- .bashrc
- .bash_aliases
Open Mac Terminal
What happens when you start Terminal?
Terminal runs a program called bash located in /bin/bash or /user/bin/bash or //usr/local/bin/bash
To see where execute
which bash
bash reads the .bash_profile script in your home directory.
What's in .bash_profile?
Execute
# ~ is the home directory of the user account. \\ cat ~/.bash_profile # or # bbedit .bash_profile
You should see this
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then source ~/.bashrc fi
Notes:
fi ends the if block.
The -f flag checks for the existence of a file named ~/.bashrc.
If it is found then source /~//.bashrc is run.
The source command reads and executes any commands in .bashrc.
Check in Terminal
ls /Volumes
You should see cs312-00-w20
You should not see COURSES
ls -lR /Volumes/cs312-00-w20
-lR (long Recursive)
What's in .bashrc
Execute
bbedit ~/.bashrc # or # cat .bashrc
You should see this
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then source ~/.bash_aliases fi export PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:$PATH" export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups # needed by VS Code to override an error message # see last comment on https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-cpptools/issues/1445 export CPPTOOLS_DEV=1 # useful commands ## from http://linuxcommando.blogspot.com/2008/04/quick-hex-decimal-conversion-using-cli.html htod () { printf '%d\n' $1; } dtoh () { printf '0x%x\n' $1; } setup312() { if [ 1 -ne $# ]; then echo "Usage:\tsetup312 <your_carleton_email_name>" exit 1 fi student=$1 coursefolder=/Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork export HOME312=$coursefolder/$student echo "export PATH=$HOME312/bin:$PATH" >> /Users/labuser/.bashrc cd $HOME312 source ~/.bashrc }
Notes:
- source ~/.bash_aliases
- Reads the .bash_aliases script that contains shortcuts for commands that take a long time to type.
cl is the short form of clang++ -std=c++17 -Wall , the compile command for C++.
-Wall is Warnings all. - export
- Creates a shell variable and makes it available to other scripts in the shell environment.
When used in other scripts variables are prefixed with $ after they are declared or exported. - export PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:$PATH"
- The directories /usr/local/bin and /usr/local/sbin are prepended to $PATH.
- export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
- It's easy to recall previous commands using the up and down arrows.
ignoredups removes duplicate commands from the history list. - export CPPTOOLS_DEV=1
- Needed by vsCode.
- htod and dtoh are bash functions
# decimal to hex dtoh 144 #hex to decimal htod 0x90
- setup312() is another bash function
- Read the comments.
setup312() { # if 1 (true) is -ne (not equal) to $# (the number of command line parameters to the function) # echo a usage message to Terminal and exit if [ 1 -ne $# ]; then echo "Usage:\tsetup312 <your_carleton_email_name>" exit 1 fi # If we get here there was one parameter, your_carleton_email_name # define but do not export the variable student to be $1 (parameter 1) # $student does not exist outside this function # parameter 1 is your_carleton_email_name student=$1 # define the variable course folder to be /Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork coursefolder=/Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork # export the HOME312 variable to the shell environment as $coursefolder/$student export HOME312=$coursefolder/$student # prepend the $HOME312/bin folder to the $PATH variable # >> writes that line back to .bashrc after any existing text echo "export PATH=$HOME312/bin:$PATH" >> /Users/labuser/.bashrc # now if you open a second terminal or tab $PATH will include your /Volumes/cs312-00-w20/StuWork/bin folder # cd (change directory) to $HOME312 cd $HOME312 # execute commands in ~/.bashrc to capture what setup312 just did source ~/.bashrc }
Note:
The setup312 function is not executed when .bashrc is read.
It is only executed when you type setup312 <your_carleton_email_name> on the command line.
You can edit and re-source .bashrc while you're logged in.
What's in .bash_aliases
alias cd312="cd $HOME312/cs312" alias rm="rm -i"; # interactive remove alias ls="ls -GFh"; alias clang++="clang++ -std=c++17 -Wall "; alias cl="clang++ -std=c++17 -Wall "; alias cld="clang++ -g -std=c++17 -Wall "; alias cmake="/usr/local/bin/cmake"
-g generates debug information needed by the debugger.